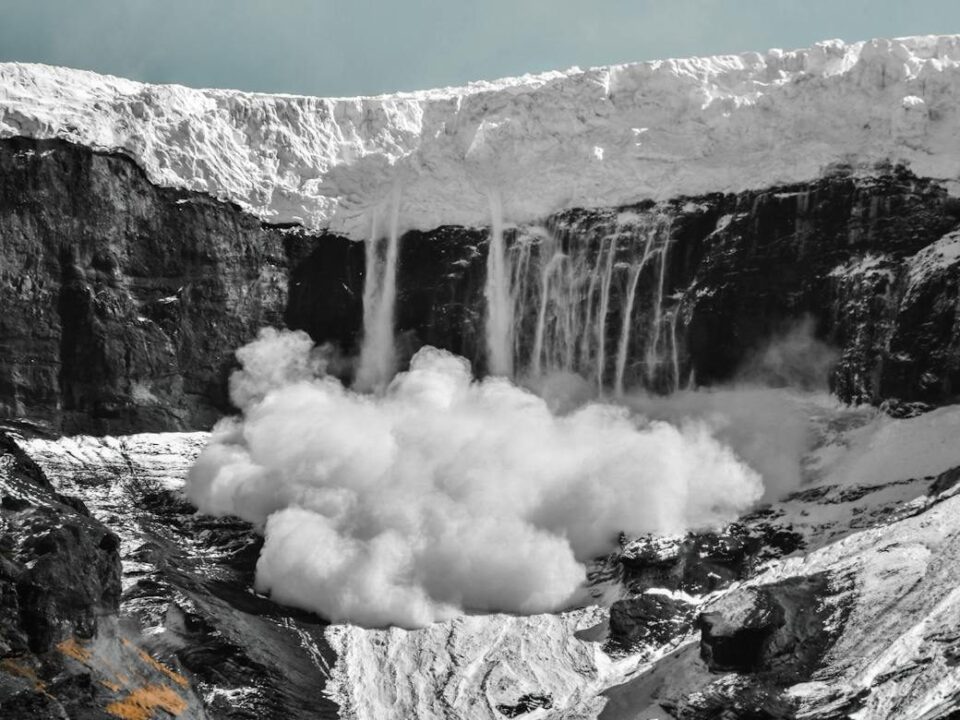
Avalanches, powerful and unpredictable, pose significant risks to individuals exploring mountainous terrains. To navigate these hazards, it’s crucial to delve into the science behind avalanches, recognize potential signs, understand vulnerable areas, and adopt safety measures to mitigate risks.
Table of Contents

Also read: Understanding Earthquakes: Nature’s Unpredictable Force
The Science Behind Avalanches
Avalanches occur when a mass of snow breaks loose from a mountain slope and descends rapidly. Several factors contribute to avalanche formation, including:

Snowpack Stability: The stability of the snowpack is critical. Layers of different snow types, such as weak, sugary snow over stronger, cohesive layers, can create instability, leading to avalanches.
Terrain: Steep slopes, often above 30 degrees, are more prone to avalanches. Additionally, specific features like convexities, couloirs, and cornices can increase the likelihood of an avalanche.
Weather Conditions: Heavy snowfall, rapid temperature changes, or rain on snow can elevate the risk of avalanches. These weather events affect snowpack stability and contribute to the accumulation of a critical mass.
Occupancy and Vulnerable Areas
Understanding where avalanches are likely to occur is crucial for those venturing into mountainous regions. High-risk areas include:
Backcountry: Off-piste skiing, snowboarding, or hiking in uncontrolled, remote areas heighten the risk of encountering avalanches.
Mountain Passes: Popular routes through mountain passes can be susceptible to avalanches, especially during and after snowstorms.
Alpine Meadows: These areas, often appealing for recreational activities, can become avalanche-prone due to factors like wind-loading and snow accumulation.
Early Signs and Warning Indicators
Recognizing early signs of potential avalanches is key to avoiding life-threatening situations:
Recent Avalanches: Observing recent avalanche activity in the area indicates instability and heightened risk.
Cracking Sounds: Audible cracking or collapsing noises in the snowpack suggest stress and instability.
Recent Weather Events: Rapid changes in weather, such as heavy snowfall, warming temperatures, or rain, increase the likelihood of avalanches.
Safety Measures
To minimize the risks associated with avalanches, individuals should adhere to essential safety measures:
Education: Acquire knowledge through avalanche safety courses, learning about terrain assessment, snowpack evaluation, and rescue techniques.
Avalanche Gear: Always carry essential avalanche safety gear, including a transceiver, probe, and shovel. These tools are critical for rescue operations.
Terrain Management: Evaluate the terrain, identify potential hazards, and avoid high-risk areas during periods of elevated avalanche danger.
Group Communication: Maintain effective communication within your group. Establish clear signals and adhere to safe travel practices.
Weather Monitoring: Stay informed about weather conditions, avalanche forecasts, and recent snowpack observations to make informed decisions.
Conclusion
Avalanches demand respect and caution from those exploring snow-covered landscapes. By understanding the science behind avalanches, recognizing vulnerable areas, and implementing safety measures, individuals can enjoy winter activities while minimizing the inherent risks associated with these powerful natural events. Education, awareness, and preparedness are paramount in navigating the snowy expanses responsibly.
Join our WhatsApp channel for the latest updates, here.